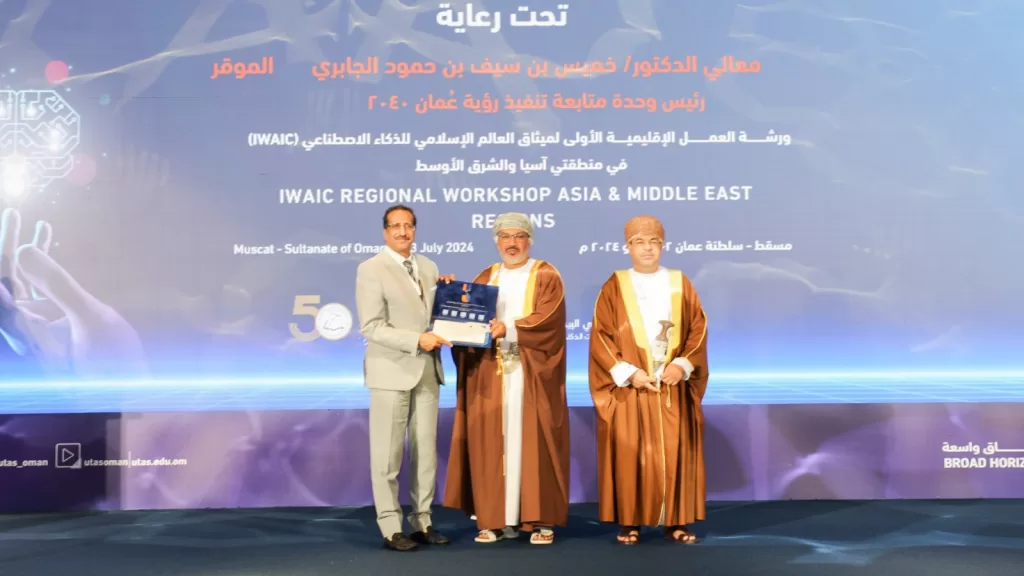
On Wednesday, July 3rd, 2024, the Islamic World AI Charter for Asia and Middle East Regions Workshop concluded its proceedings. The two-day workshop featured rich discussions and an exchange of ideas among a select group of officials, experts, and representatives of ICESCO Member States. They presented the results of their discussions on the ethical principles of artificial intelligence to be included in the Charter, as well as their proposals for oversight and governance mechanisms to ensure the proper application of these principles.
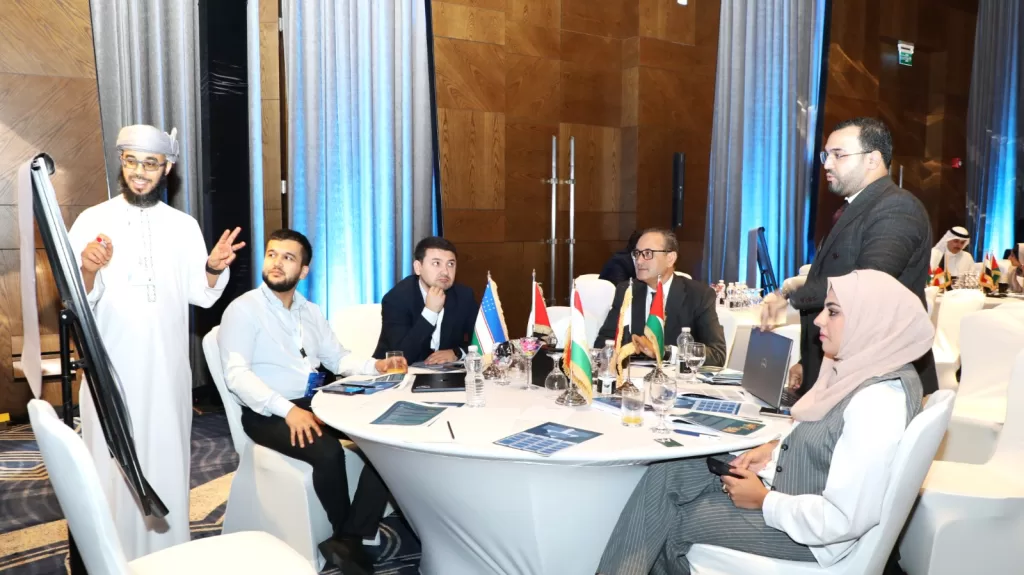

Participants in this workshop, organized by the Islamic World Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (ICESCO), in partnership with the University of Technology and Applied Sciences (UTAS) and the Ministry of Transport, Communications and Information Technology of Oman, and in collaboration with the Omani National Commission for Education, Culture and Science, emphasized the necessity of drafting legal and ethical frameworks to govern artificial intelligence. The participants also stressed the need to carry this out in tandem with building human capacities to use AI and the importance of aligning the Islamic World Charter for Artificial Intelligence with international charters, while considering the specificities and values of the Islamic world. Moreover, they called for balancing innovation and scientific research with the protection of individual rights, stressing the importance of awareness-raising and capacity-building.

At the beginning of the second day of the Workshop, held as part of the activities of ICESCO Chair for Artificial Intelligence Ethics at UTAS in Oman and in preparation for the Islamic World Charter for Artificial Intelligence, Dr. Salim M. AlMalik, ICESCO Director General, gave his remarks prior to the start of the working group discussions, where he underscored the necessity of integrating an ethical value system into the Charter to achieve its intended purpose, with a focus on creativity, individual freedom, and equity.
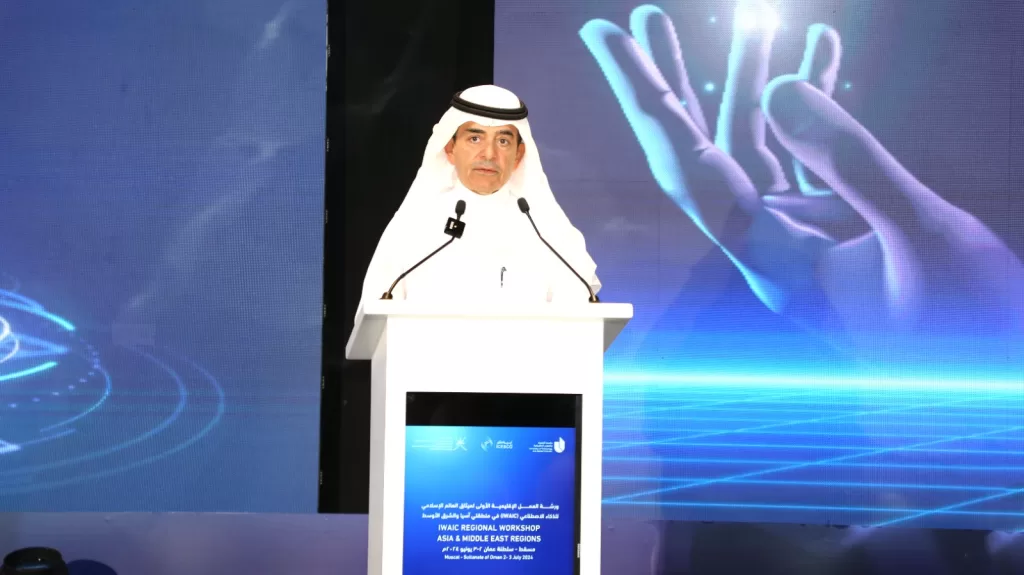

Dr. AlMalik added that although the application of artificial intelligence across various domains yields substantial advantages, its unethical use poses significant risks, such as its use in preparing research and studies for academic degrees, which represents a form of academic plagiarism and corruption.
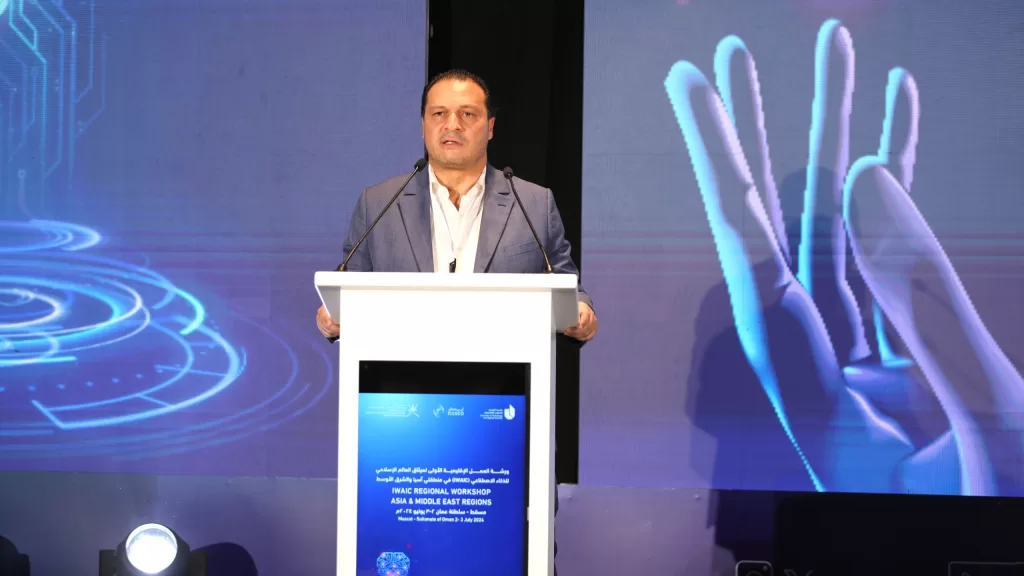

In his statement, Dr. Kais Hammami, Head of ICESCO’s Center for Foresight and Artificial Intelligence, reviewed the Center’s efforts and methodology in promoting the culture of foresight, foundational principles of methodological analysis, dynamic scenario building, and the use of the Arabic language in this domain.
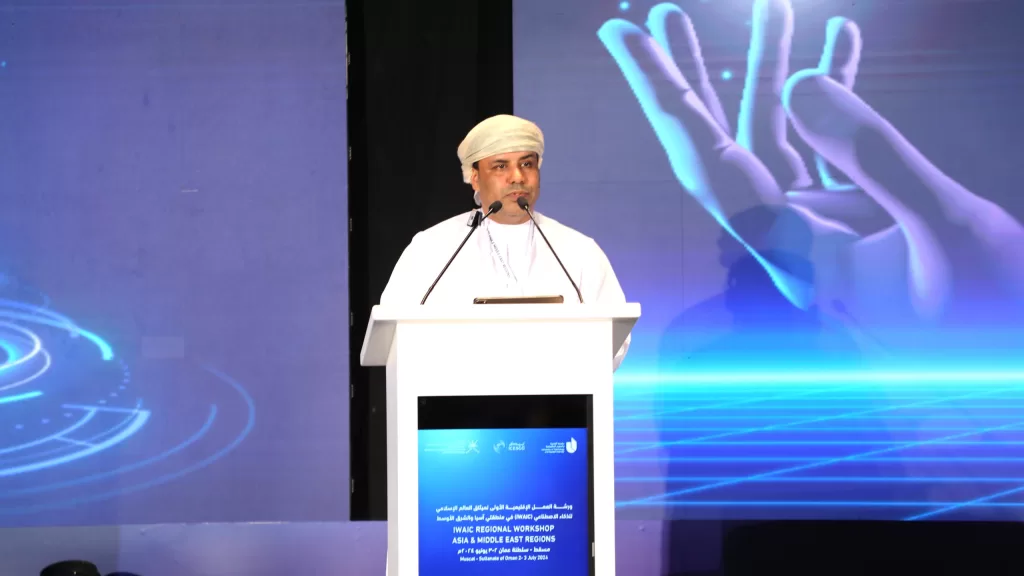

Speaking next, Dr. Said Bin Salem Jaboob, Deputy Vice Chancellor of UTAS for Postgraduate Studies, Research, and Innovation, stated that preparing the initial draft of the Charter’s articles is a significant step towards establishing a solid framework for AI ethics and governance in Asia and the Middle East.

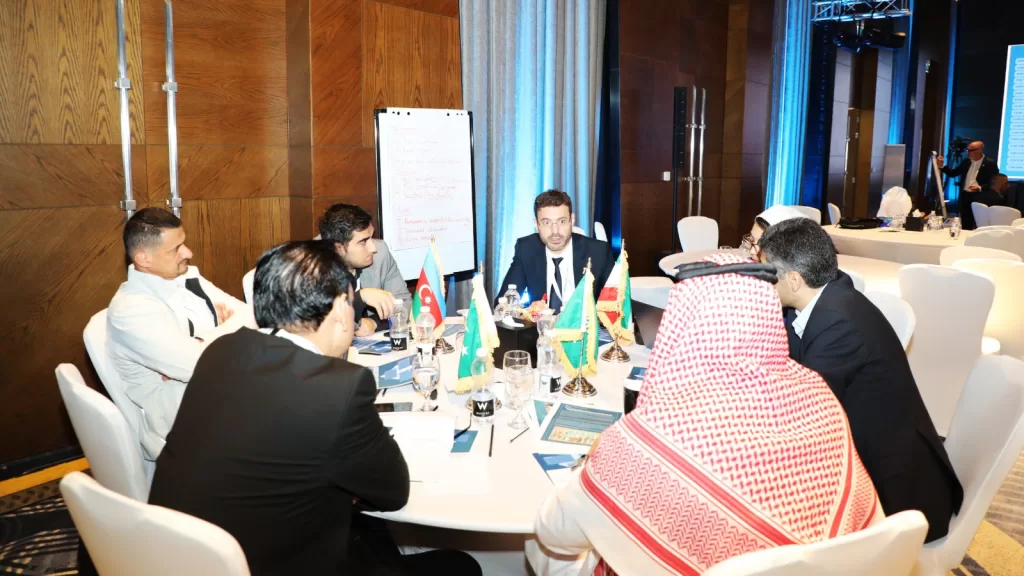
The second day’s agenda included brainstorming sessions to develop a comprehensive vision for the Islamic World Charter for Artificial Intelligence. Experts and researchers were divided into four groups, each discussing multiple scenarios to derive several ethical principles necessary for better drafting of the Charter.